Solar panels, also known as solar cell panels or PV modules, are devices that convert sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) cells.
These panels are widely used for residential, commercial, industrial, space, and transportation applications.
According to the 2023 Heatmap Climate Poll, 46% of American adults express an interest in using solar panels to generate electricity for their homes in the future, while 13% are already utilizing this technology.
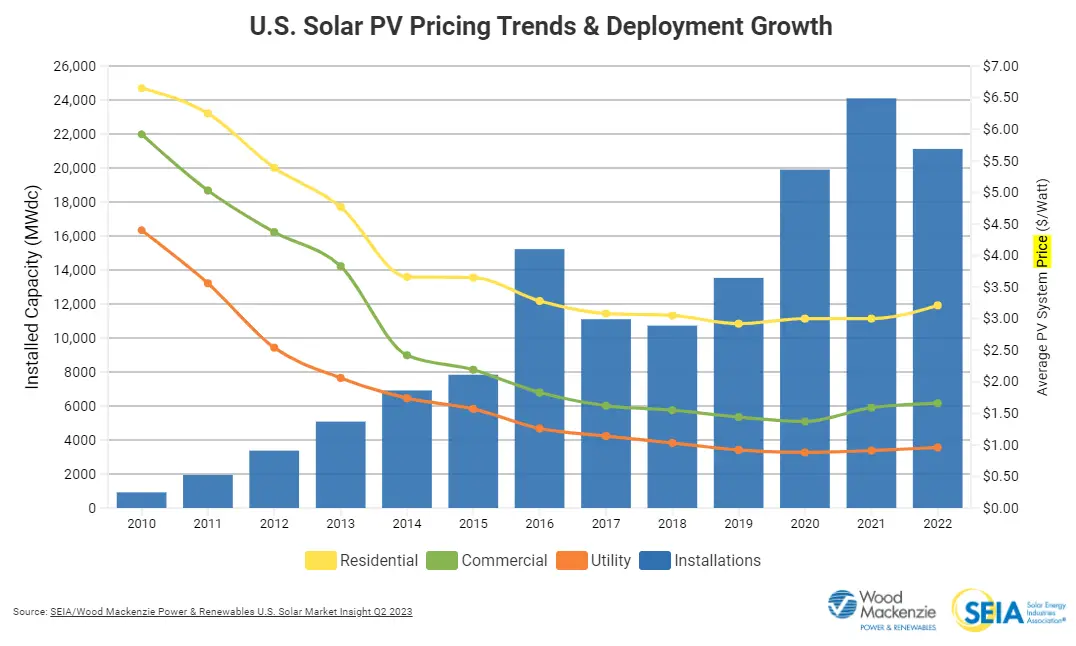
The solar industry has witnessed significant growth and technological advancements over the past few decades, leading to decreased solar panel prices.
Since 2010, residential solar panel costs have decreased by approximately half, while solar installation in the United States has surged by more than 2,000%.
However, the overall cost isn’t just about the panels themselves.
Average Cost of Solar Panels
The average cost of solar panels is affected by the solar panel types you use.
The cost of premium monocrystalline solar panels typically ranges in price from $1 to $1.50 per watt.
Consequently, the cost of a single 400-watt solar panel falls within the range of $400 to $600.
On the other hand, less efficient polycrystalline panels are generally more budget-friendly, priced at around $0.75 per watt.
Thus, a 400-watt panel would cost approximately $300.
In 2023, the average cost of complete residential solar panel installation in the U.S. ranges between $17,430 and $23,870 after federal tax credits, with a price per watt ranging from $2.50 to $3.50 depending on the geographical area.
Average Cost Of Solar System
The cost of a fully installed solar system generally ranges from $3 to $5 per watt before incentives like the 30% tax credit.
Therefore, a 5,000-watt (5 kW) solar system would have a gross cost between $15,000 and $25,000.
The price per watt for larger and straightforward projects typically falls within the $3-$4 range. Applying incentives such as tax credits and rebates can further reduce the price per watt.
However, certain factors may increase your solar price per watt to the $4 to $5 range.
These factors include smaller system size, unusual roof material or layout, premium panel, and inverter models, multiple arrays versus a single array, and additional work like panel box upgrades, trenching, or roof repair.
Average Cost of Hybrid Solar System with Battery Storage
The average cost of a residential solar system is typically for a grid-tied system, with an average 7 kW system priced at around $21,000 excluding battery storage.
For hybrid systems that include a battery backup, an additional $10,000 is expected to be added to the installation cost.
This brings the average cost of a hybrid system to about $31,000 before any federal tax credits.
With these tax credits, the cost of the system can be reduced to approximately $21,700.
However, installation prices can vary depending on the brand and the number of batteries installed.
For instance, a Tesla Powerwall, offering 13.5 kWh of storage, costs around $12,850, whereas an LG Chem, offering 9.8 kWh of storage, costs about $11,000.
Installation Cost of Off-Grid Solar Panel System
Off-grid solar systems are notably more costly than grid-tied and hybrid solar systems due to the need for more solar panels and larger battery storage capacity.
This is because there is no grid to rely on during periods of low solar generation or high electricity consumption.
A standard off-grid system for a family home aiming for a relatively normal lifestyle typically costs between $50,000 to $70,000 before applying the federal tax credit.
After deducting the current 30% tax credit, the cost ranges from $35,000 to $49,000.
Average Solar Panel Cost Per Square Foot
The cost of solar panels for homes can be roughly estimated based on the costs for similar homes, although this method is the least accurate.
An analysis of thousands of systems sold on solar.com in 2022 revealed that on average, solar panels cost $8.77 per square foot of living space after factoring in the 30% tax credit.
However, the cost per square foot fluctuates depending on the size of the home.
For instance, a 2,500-square-foot home would have a post-tax credit cost of around $20,000 for solar panels, equating to $7.96 per square foot.
Conversely, a 1,500-square-foot home would have an average system cost that is only $1,000 lower, yet the cost per square foot increases to $12.83.
While discussing with friends, family, and neighbors who have installed solar systems can provide some insights into the pros, cons, and costs, these figures offer a more precise understanding of potential costs.
Average Cost of Building Solar Farm
First thing first, we should know that the cost per watt for setting up a solar farm and a residential solar system is not the same.
Residential solar systems tend to be more expensive on a cost-per-watt basis due to the complexity and variety of residential installations, which can include factors such as roof type, home orientation, local permitting costs, and aesthetic choices.
On the other hand, solar farms, also known as utility-scale solar installations, typically have a lower cost per watt because they benefit from economies of scale.
They involve the installation of a large number of panels in one location, which leads to lower installation costs per unit and more straightforward logistics.
The typical cost of building a solar farm is between $0.89 and $1.01 per watt. A 1MW (megawatt) solar farm can cost you between $890,000 and $1.01 million.
If you have the land to build a solar farm, these costs are based on the SEIA’s average national cost numbers.
Solar Panel Financing Options: Cash Payment, Solar Loan, or Solar Lease
Various solar financing options for solar panels are available depending on your installation service, such as paying upfront in cash, securing a solar loan, opting for a solar lease, or entering into a power purchase agreement (PPA).
To maximize your return on investment, we suggest either purchasing your solar panels outright or utilizing a loan to spread the cost over time.
While solar leases and PPAs may offer low initial expenses, homeowners generally save less over the long term compared to owning their solar energy system.
Furthermore, leasing or entering a PPA means you won’t own the system, making you ineligible for specific incentives like the federal solar tax credit.
Factors That Impact Solar Electricity Production
Shade: Solar panels perform best in direct sunlight. If your roof is shaded by trees or buildings that can’t be trimmed, solar may not be the most efficient choice.
Seasonality: Solar energy production varies with the weather and seasons.
While cloudy, winter days are less productive than sunny, summer ones, it’s important to consider year-round performance.
For instance, snow can reflect light and improve photovoltaic (PV) performance unless the panels are covered by slush.
Tilt: The effectiveness of solar panels can be influenced by the direction your home faces, its location, and your roof’s pitch.
Ideally, solar panels should be angled at the same degree as the latitude where they’re installed, with pitches between 30 and 45 degrees typically working well.
Azimuth: This is the compass direction from where sunlight is coming.
Incorrect azimuth angles can reduce a solar panel’s energy output by up to 35%. Typically, an azimuth of zero (facing the equator) is the best choice.
Why Solar Batteries Add New Complexity to Estimating Average Solar System Cost?
Before 2020, over 90% of residential solar power installations were grid-tied solar systems, mainly because they were the most affordable to install and provided the shortest payback period.
However, these systems lack a backup power source during power outages.
As a result, many people are considering adding a solar battery to their solar systems in 2023 for four main reasons:
- Increased demand for a backup power supply due to the rising frequency of storms and wildfires, which have made utility power less reliable.
- Changes in net metering programs by utilities across the country are offering below-retail rates for excess solar energy production sent to the grid.
- The adoption of Time of Use electric billing makes home energy storage solutions more attractive. Batteries can be charged when utility rates are cheap and discharged when rates are high, allowing homeowners to avoid peak pricing.
- The 30% solar investment tax credit can be applied to a battery as long as it’s connected to a solar power system. Additionally, there are several state and utility incentives, like California’s SGIP incentive, which help reduce the cost of battery installations.
How Do State-Specific Costs Affect Solar Panel Installation Pricing?
State-specific costs are crucial as they are influenced by regional electricity rates, solar incentives, and other local factors.
For instance, the average cost for a 6-kW solar system varies across states – in Pennsylvania, it’s around $11,411, while in South Carolina, it’s about $12,210 after federal tax credits.
These costs are further influenced by the local cost of grid power and the average household electricity usage, which ultimately impacts the savings and the payback period for solar investments.
How Do Local Incentives And Rebates Affect The Cost Of Solar Panels?
Government incentives and subsidies can help offset the cost of installing solar panels.
In the United States, there is a federal tax credit of up to 30% of the system’s cost.
It’s important to research and understand the available subsidies and incentives in your specific location.
What Is The Range Of Costs For Different Types And Sizes Of Solar Panel Systems?
The cost of solar panel systems varies widely based on their type and size.
For example, a medium-scale solar panel system (5 kW) for larger homes or small businesses may cost between $15,000 and $25,000, while large-scale systems (over 7 kW) for commercial properties can range from $25,000 to $50,000 or more.
Moreover, the overall cost can range from $4,500 to $36,000 depending on the type, model, and the balance of system components included.








