A solar farm is a vast area of land where lots of solar panels are set up to collect sunlight and change it into electricity.
Solar farms have various types. Unlike a small number of solar panels on a roof, a solar farm has many more panels spread out over a large area and has the capacity to generate electricity for thousands of homes.
The development of large-scale solar farms has increased exponentially in recent years as countries aim to transition to renewable energy sources.
On a global scale, the solar farm market, valued at USD 61 billion in 2022, is projected to move to around USD 299.53 billion by 2032.
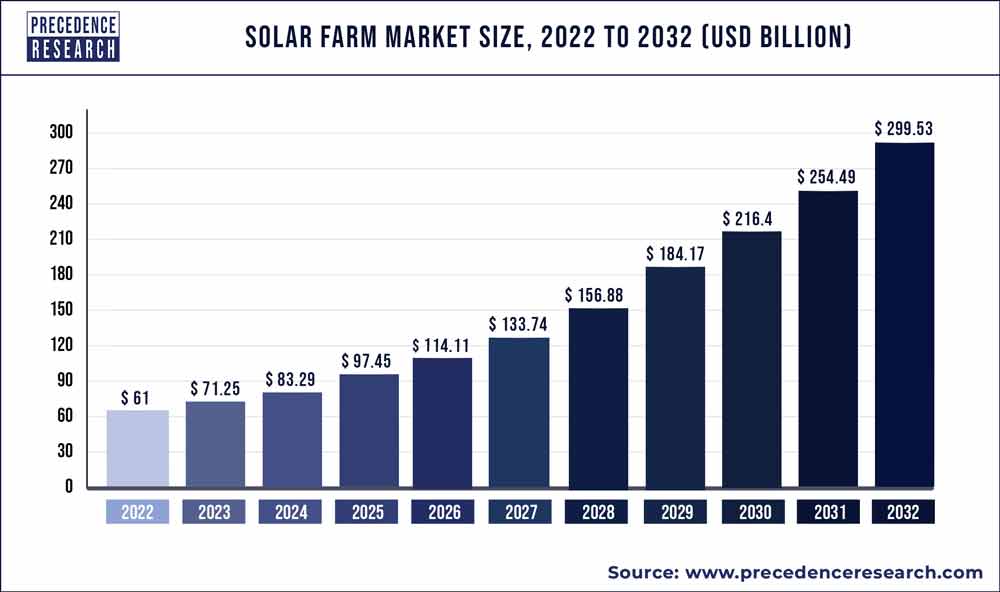
This growth, representing a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 17.3% from 2023 to 2032, emphasizes the escalating development and investment in solar farms.
The US solar industry is expected to add a record 32 gigawatts of new capacity in the year 2023, which is a 52% increase from the year 2022.
As the solar farm industry experiences growing popularity, it’s important to note that lease rates for solar farm land can vary widely.
Typically, these rates range from $250 to $2,000 per acre per year, and they are influenced by factors like the geographical location of the land and its overall quality.
What Is A Solar Farm?
A solar farm, also known as a photovoltaic (PV) power station or solar park, is a large-scale installation of solar panels designed to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity.
These facilities play a vital role in the transition towards renewable energy sources, helping to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Solar farms can be developed on unused or underutilized land, such as agricultural fields, brownfields, or desert areas, using the available space to maximize energy production.
Solar farms consist of numerous solar panels strategically arranged to capture the maximum amount of sunlight throughout the day.
These panels contain photovoltaic cells that convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. This DC electricity is converted into alternating current (AC) through inverters, making it compatible with the electrical grid.
The generated electricity can be used for various purposes, including powering homes, businesses, and public facilities, or it can be sold back to the grid for profit.
How Does A Solar Land Lease Work?
A solar land lease is a contractual agreement between a landowner and a solar farm developer, allowing the developer to use the land to construct and operate a solar farm.
In return, the landowner receives a steady stream of income through lease payments for the duration of the contract.
Solar land leases typically last for 20 to 30 years, with options to extend the lease term, depending on the continued viability of the solar farm.
The leasing process usually begins with the developer conducting a feasibility study to assess the suitability of the land for a solar farm.
Factors such as sun exposure, topography, soil quality, and proximity to electrical infrastructure are considered to determine the site’s potential.
If the land is deemed suitable, the parties negotiate the terms and conditions of the lease, including the payment structure and any necessary permits or approvals.
Lease payments can be structured in various ways, such as a fixed annual payment or a payment based on the solar farm’s energy production.
Some leases may also include escalator clauses, adjusting the lease rate over time to account for inflation or changes in the energy market.
Ultimately, a solar land lease can provide landowners with a stable, long-term income source while contributing to the growth of clean energy infrastructure.
Important Factors Determining The Solar Farm Lease Rates
Location
The geographical location of the land plays a crucial role in determining solar farm lease rates.
Areas with higher sun exposure and longer daylight hours are more attractive to solar developers, as they have the potential for greater energy production.
Additionally, proximity to existing electrical infrastructure, such as transmission lines and substations, can also impact the lease rates, as it reduces the cost of connecting the solar farm to the grid.
Land Size And Topography
The size of the land and its topography are essential factors that influence lease rates.
Larger, contiguous plots of land are more desirable, as they can accommodate more solar panels and generate more power.
Similarly, flat or gently sloping land is preferred over steep or uneven terrain, as it simplifies installation and reduces construction costs.
Soil Quality
The soil quality on the land can affect lease rates, as it determines the ease of installation and the potential impact on agricultural productivity.
Developers prefer land with soil that allows for easy installation of solar panel mounting structures while minimizing the disturbance to the land’s fertility.
In some cases, developers might pay a premium for land with lower agricultural value but are well-suited for solar farm construction.
Zoning And Permitting
The ease of obtaining permits and complying with local zoning regulations is another factor that influences lease rates.
Land situated in areas with streamlined permitting processes and favorable zoning regulations for solar development is more attractive to developers and can command higher lease rates.
Conversely, land with restrictive zoning or complicated permitting requirements may result in lower lease rates or make it less likely for developers to pursue a project.
Regional Policies And Incentives
State and local policies, such as renewable energy mandates, tax incentives, or feed-in tariffs, can significantly impact solar farm lease rates.
In regions with strong policy support for solar energy, developers may be more willing to invest in projects and offer higher lease rates to secure land.
On the other hand, areas with limited policy support or fewer incentives may see lower lease rates due to reduced demand for solar development.
Market Conditions
The overall market conditions for solar energy, including the cost of solar panels, the price of electricity, and the availability of financing, can affect lease rates.
When market conditions are favorable and the demand for solar energy is high, developers may be more inclined to offer higher lease rates to secure prime land for their projects.
Conversely, unfavorable market conditions or a downturn in the solar industry may lead to reduced demand for land and lower lease rates.
What Is The Land Area Requirement For A 1 MW Solar Power Plant?
The area required for a solar farm depends on panel efficiency and available sunlight.
On average, a 1 MW solar farm would need between 5 to 10 acres, a 5 MW solar farm would need between 25 to 50 acres, and so on.
This estimation, however, can vary based on the efficiency of the solar panels used and the specific conditions of the installation site, such as sunlight hours and local climate.
What Is The Lifespan Of Solar Farm?
Solar farms, or the solar panels used in them, typically have a lifespan of around 25 to 30 years.
This doesn’t mean they stop producing electricity after this time, but rather that their energy production significantly decreases after these years.
It’s estimated that solar panels lose about 1% of their effectiveness each year, so by the end of their 25-30-year lifespan, they’ll be operating at around 75-80% of their original capacity.
However, with proper maintenance and care, some panels can last longer than the typical lifespan. The inverters, which convert solar power into usable electricity, typically need to be replaced every 10 to 15 years.
Is Leasing Land For Solar Farms Profitable?
Leasing land for solar farms can be a profitable decision.
Landowners who lease their land for solar farms can earn between $250 to $2,000 per acre per year.
Additionally, solar farms typically cost between $0.89 to $1.01 per watt to install, and a 1 MW farm can earn roughly $43,500 a year by selling its electricity to utilities.
How Do Solar Farm Land Rental Rates Compare To Agricultural Land Leasing Rates?
Solar farm land rental rates often surpass traditional agricultural leasing rates.
While farming lease rates are determined by soil quality and crop yields, solar rental rates are primarily influenced by location, sunlight availability, and proximity to infrastructure.
In many instances, landowners can receive a higher and more stable income from solar leases compared to agricultural leases, making it an attractive alternative, especially in areas with less fertile soil or challenging farming conditions.
Does Leasing Land For A Solar Farm Affect Its Resale Value?
Leasing land for a solar farm can influence its resale value.
Properties with active, long-term solar leases might be more attractive to investors or buyers who prioritize steady revenue streams.
However, potential buyers might also consider the duration left on the lease and the terms of land restoration post-decommissioning.
It’s essential for landowners to maintain clear, favorable lease terms to ensure that the property remains an attractive buy in the real estate market.
How Long Are Typical Solar Land Lease Agreements?
Solar land lease agreements are typically long-term, ranging from 15 to 30 years.
This is because they mirror the productive lifespan of solar installations.
However, these agreements often include provisions for extensions, ensuring that if the panels remain efficient, the energy production can continue seamlessly.








